Connective Tissue Cells | Based on the cells present and the ecm structure, we differ two types of. Connective tissue cells are able to reproduce but not as rapidly as epithelial cells. Specialized connective tissue encompasses a number of different tissues with specialized cells and unique ground substances. Specialized cells in connective tissue defend the body from microorganisms that enter the body. During embryonic development, undifferentiated mesenchymal cells, derived from mesodermal and mesectodermal (neural crest cells) origins, give rise to the different.
Connective tissue consists of scattered cells immersed in an intercellular material called the matrix. When damage occurs in connective tissue, there are two stages of response. There are three main components to connective tissue: Connective tissue makes up a connective tissue has relatively few cells separated by a large amount of extracellular matrix (as. Connective tissue cells are able to reproduce but not as rapidly as epithelial cells.
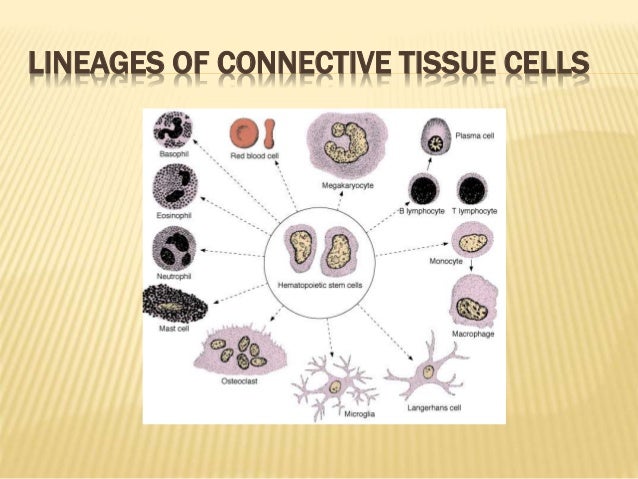
Connective tissue consists of specialized cells that are embedded in the extracellular matrix (ecm). Connective tissue supports, connects, binds, or separates other tissues or organs. Connective tissue cells are able to reproduce but not as rapidly as epithelial cells. Some are solid and strong, while others are fluid and flexible. These cells in osseous tissue are known as osteocytes. Specialized cells in connective tissue defend the body from microorganisms that enter the body. There are three main components to connective tissue: The cells are of different types the extra cellular matrix has nearly amorphous ground substance which is made of glycoproteins with associated mucopolysaccharides. Connective tissue is one of the four types of tissue in traditional classifications (the others being epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissue.) it is characterized by abundant extracellular matter (intercellular substances and fibers) encasing relatively few cells. Also, these tissues perform other function that helps in the various mechanism of the body. Connective tissue is the most diverse and abundant tissue type. In addition to the relatively fixed cell types described above, there are free cells that reside in the interstices of loose connective tissue. When damage occurs in connective tissue, there are two stages of response.
Also, these tissues perform other function that helps in the various mechanism of the body. Fundamental cell types, characteristic of each kind of connective tissue, are responsible for. Connective tissue it consist 3 types of components: During embryonic development, undifferentiated mesenchymal cells, derived from mesodermal and mesectodermal (neural crest cells) origins, give rise to the different. Then we have osseous tissue or bone tissue.

Fibrous connective tissue, however, does not contain any living cells, as its main function is support and. Connective tissues provide a matrix that supports and physically connects other tissues and cells together in organs. Learn about connective tissue cell with free interactive flashcards. A fat cell is a spherical cell that contains a large cytoplasmic droplet filled with oils, or fat. Connective tissue is classified as loose or dense connective tissue depending on the ratio and. Connective tissue is distinguished from the other types in that the extracellular material (matrix) usually occupies more space than the cells do, and the cells are relatively far apart. Fibroblasts, adipocytes (fat cells), macrophages, and mast cells are regarded as resident cells. Connective tissue is the most diverse and abundant tissue type. Based on the cells present and the ecm structure, we differ two types of. Macrophage and mononuclear phagocyte system. Connective tissue cells that produce unusually large amounts of contractile proteins are termed myofibroblasts. The fibers and ground substance of connective tissue create what is known as the extracellular matrix. Fundamental cell types, characteristic of each kind of connective tissue, are responsible for.
Connective tissue supports, connects, binds, or separates other tissues or organs. Plasma cells may also be foundwithin the connective tissue of many of the glands that secrete into these regions. Learn about connective tissue cell with free interactive flashcards. Fibrous connective tissue, however, does not contain any living cells, as its main function is support and. Identify and list the cell types found in the various kinds of general connective tissues, and describe their.

2) fibers of connective tissus. Connective tissue cells that produce unusually large amounts of contractile proteins are termed myofibroblasts. Macrophage and mononuclear phagocyte system. Collagen fibroblasts and fatty cells; Connective tissue — noun tissue of mesodermal origin consisting of e.g. Epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Three of the most common are the fibroblast, macrophage, and. There are three main components to connective tissue: These cells in osseous tissue are known as osteocytes. Supports organs and fills spaces between them and forms tendons and ligaments (freq. Also, these tissues perform other function that helps in the various mechanism of the body. Connective tissue consists of specialized cells that are embedded in the extracellular matrix (ecm). It consists of connective tissue cells embedded in a large amount of extracellular matrix.
The interstitial fluid of connective tissue gives metabolic support to cells as the connective tissue. Fibrous connective tissue, however, does not contain any living cells, as its main function is support and.
Connective Tissue Cells: In tendon and bone, the collagen fibers are arranged in very precise order to provide very robust tensile strength.
Source: Connective Tissue Cells